Exercise 1: Make a Processing Etch-A-Sketch
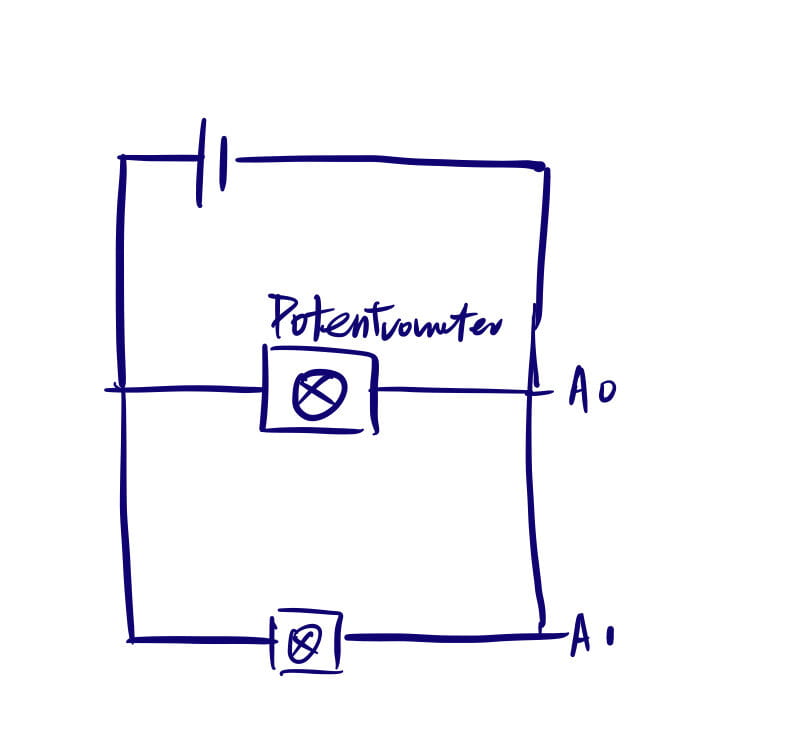
Video:
Code(Arduino):
// IMA NYU Shanghai // Interaction Lab // For sending multiple values from Arduino to Processing void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // to send values to Processing assign the values you want to send //this is an example int sensor1 = analogRead(A0); int sensor2 = analogRead(A1); // int sensor3 = analogRead(A2); // send the values keeping this format Serial.print(sensor1); Serial.print(","); // put comma between sensor values Serial.print(sensor2); // Serial.print(","); // put comma between sensor values // Serial.print(sensor3); Serial.println(); // add linefeed after sending the last sensor value // too fast communication might cause some latency in Processing // this delay resolves the issue. delay(100); // end of example sending values }
Code(Processing):
// IMA NYU Shanghai // Interaction Lab // For receiving multiple values from Arduino to Processing /* * Based on the readStringUntil() example by Tom Igoe * https://processing.org/reference/libraries/serial/Serial_readStringUntil_.html */ import processing.serial.*; int num = 60; float px; float x; float py; float y; //float speed = abs(x0-px) + abs(y0-py); int NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO = 2; /** YOU MUST CHANGE THIS ACCORDING TO YOUR PROJECT **/ int sensorValues[]; /** this array stores values from Arduino **/ String myString = null; Serial myPort; void setup() { size(500, 500); background(0); setupSerial(); } void draw() { getSerialData(); printArray(sensorValues); x=map(sensorValues[0],0,1023,0,500); y=map(sensorValues[1],0,1023,0,500); stroke(255); line(px, py, x, y); px=x; py=y; } // add your code // void setupSerial() { printArray(Serial.list()); myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[ 2 ], 9600); // WARNING! // You will definitely get an error here. // Change the PORT_INDEX to 0 and try running it again. // And then, check the list of the ports, // find the port "/dev/cu.usbmodem----" or "/dev/tty.usbmodem----" // and replace PORT_INDEX above with the index number of the port. myPort.clear(); // Throw out the first reading, // in case we started reading in the middle of a string from the sender. myString = myPort.readStringUntil( 10 ); // 10 = '\n' Linefeed in ASCII myString = null; sensorValues = new int[NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO]; } void getSerialData() { while (myPort.available() > 0) { myString = myPort.readStringUntil( 10 ); // 10 = '\n' Linefeed in ASCII if (myString != null) { String[] serialInArray = split(trim(myString), ","); if (serialInArray.length == NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO) { for (int i=0; i<serialInArray.length; i++) { sensorValues[i] = int(serialInArray[i]); } } } } }
Exercise 2: Tap the ball
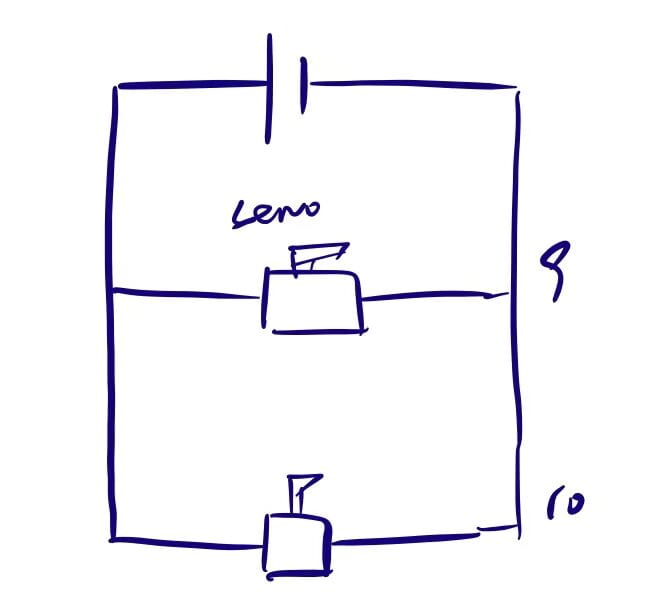
Video:
Code(Arduino):
#define NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_PROCESSING 3 #include <Servo.h> Servo myservo0; Servo myservo1; int tempValue = 0; int valueIndex = 0; int processing_values[NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_PROCESSING]; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(9, OUTPUT); pinMode(11, OUTPUT); myservo0.attach(9); myservo1.attach(10); } void loop() { getSerialData(); if (processing_values[1] == 1) { myservo1.write(90); delay(500); myservo0.write(0); } if (processing_values[0] == 1) { myservo0.write(90); delay(500); myservo1.write(0); } } void getSerialData() { while (Serial.available()) { char c = Serial.read(); //switch - case checks the value of the variable in the switch function //in this case, the char c, then runs one of the cases that fit the value of the variable //for more information, visit the reference page: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/SwitchCase switch (c) { //if the char c from Processing is a number between 0 and 9 case '0'...'9': //save the value of char c to tempValue //but simultaneously rearrange the existing values saved in tempValue //for the digits received through char c to remain coherent //if this does not make sense and would like to know more, send an email to me! tempValue = tempValue * 10 + c - '0'; break; //if the char c from Processing is a comma //indicating that the following values of char c is for the next element in the values array case ',': processing_values[valueIndex] = tempValue; //reset tempValue value tempValue = 0; //increment valuesIndex by 1 valueIndex++; break; //if the char c from Processing is character 'n' //which signals that it is the end of data case '\n': //save the tempValue //this will b the last element in the values array processing_values[valueIndex] = tempValue; //reset tempValue and valueIndex values //to clear out the values array for the next round of readings from Processing tempValue = 0; valueIndex = 0; break; } } }
Code(Processing):
import processing.serial.*; int NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_PROCESSING = 2; /** YOU MUST CHANGE THIS ACCORDING TO YOUR PROJECT **/ int processing_values[] = new int[NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_PROCESSING]; /** this array stores values you might want to send to Arduino **/ float x=1; float y; int speed=20; Serial myPort; String myString; void setup() { setupSerial(); fullScreen(); y=height/2; background(0); } void draw() { background(0); fill(255, 255, 255); circle(x, y, 50); print(y); x=x+speed; if (x<=0) { speed=speed*-1; processing_values[0] = 1; } if (x>=displayWidth) { speed=speed*-1; processing_values[1] = 1; } // give values to the variables you want to send here //change the code according to your project //for example: /* if (x=0) { processing_values[0] = 1; } else { processing_values[0] = 0; } if (x=width) { processing_values[1] = 1; } else { processing_values[1] = 0; } //processing_values[1] = mouseX; //processing_values[2] = mouseY; */ //end of example // send the values to Arduino. sendSerialData(); processing_values[0] = 0; processing_values[1] = 0; } void setupSerial() { printArray(Serial.list()); myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[2], 9600); // WARNING! // You will definitely get an error here. // Change the PORT_INDEX to 0 and try running it again. // And then, check the list of the ports, // find the port "/dev/cu.usbmodem----" or "/dev/tty.usbmodem----" // and replace PORT_INDEX above with the index number of the port. myPort.clear(); // Throw out the first reading, // in case we started reading in the middle of a string from the sender. myString = myPort.readStringUntil( 10 ); // 10 = '\n' Linefeed in ASCII myString = null; } void sendSerialData() { String data = ""; for (int i=0; i<processing_values.length; i++) { data += processing_values[i]; //if i is less than the index number of the last element in the values array if (i < processing_values.length-1) { data += ","; // add splitter character "," between each values element } //if it is the last element in the values array else { data += "\n"; // add the end of data character linefeed "\n" } } //write to Arduino myPort.write(data); print(data); // this prints to the console the values going to arduino }
Additional Homework
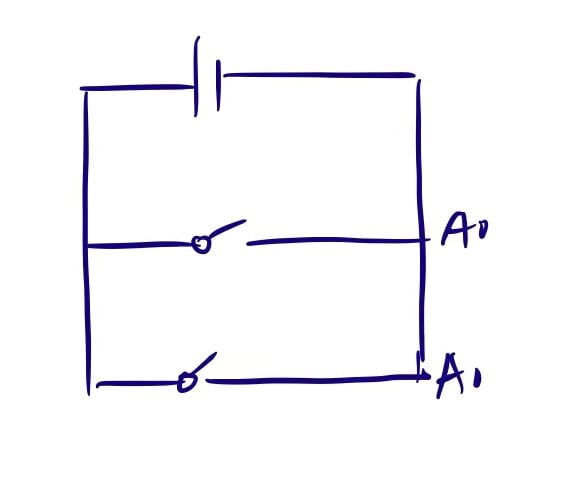
Video:
Code(Arduino):
// IMA NYU Shanghai // Interaction Lab // For sending multiple values from Arduino to Processing const int buttonPin1 = 2; const int buttonPin2 = 4; int buttonState1 = 0; int buttonState2 = 0; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(buttonPin1, INPUT); pinMode(buttonPin2, INPUT); } void loop() { // to send values to Processing assign the values you want to send //this is an example buttonState1 = digitalRead(buttonPin1); // delay(100); // buttonState1 = 0; buttonState2 = digitalRead(buttonPin2); // delay(100); // buttonState2 = 0; // // int sensor3 = analogRead(A2); // send the values keeping this format Serial.print(buttonState1); Serial.print(","); // put comma between sensor values Serial.print(buttonState2); // Serial.print(","); // put comma between sensor values // Serial.print(sensor3); Serial.println(); // add linefeed after sending the last sensor value // too fast communication might cause some latency in Processing // this delay resolves the issue. delay(100); // end of example sending values }
Code(processing):
// IMA NYU Shanghai // Interaction Lab // For receiving multiple values from Arduino to Processing /* * Based on the readStringUntil() example by Tom Igoe * https://processing.org/reference/libraries/serial/Serial_readStringUntil_.html */ import processing.serial.*; int NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO = 2; /** YOU MUST CHANGE THIS ACCORDING TO YOUR PROJECT **/ int sensorValues[]; /** this array stores values from Arduino **/ String myString = null; Serial myPort; void setup() { size(500, 500); background(0); setupSerial(); } void draw() { getSerialData(); //printArray(sensorValues); if(sensorValues[0] == 1){ star(width*0.3, height*0.3, 30, 70, 5); } else{ background(0); } if(sensorValues[1] == 1){ star(width*0.7, height*0.7, 80, 100, 40); } else{ background(0); } println(sensorValues[0], sensorValues[1]); // use the values like this! // sensorValues[0] // add your code // } void setupSerial() { printArray(Serial.list()); myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[ 2 ], 9600); // WARNING! // You will definitely get an error here. // Change the PORT_INDEX to 0 and try running it again. // And then, check the list of the ports, // find the port "/dev/cu.usbmodem----" or "/dev/tty.usbmodem----" // and replace PORT_INDEX above with the index number of the port. myPort.clear(); // Throw out the first reading, // in case we started reading in the middle of a string from the sender. myString = myPort.readStringUntil( 10 ); // 10 = '\n' Linefeed in ASCII myString = null; sensorValues = new int[NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO]; } void getSerialData() { while (myPort.available() > 0) { myString = myPort.readStringUntil( 10 ); // 10 = '\n' Linefeed in ASCII if (myString != null) { String[] serialInArray = split(trim(myString), ","); if (serialInArray.length == NUM_OF_VALUES_FROM_ARDUINO) { for (int i=0; i<serialInArray.length; i++) { sensorValues[i] = int(serialInArray[i]); } } } } } void star(float x, float y, float radius1, float radius2, int npoints) { float angle = TWO_PI / npoints; float halfAngle = angle/2.0; beginShape(); for (float a = 0; a < TWO_PI; a += angle) { float sx = x + cos(a) * radius2; float sy = y + sin(a) * radius2; vertex(sx, sy); sx = x + cos(a+halfAngle) * radius1; sy = y + sin(a+halfAngle) * radius1; vertex(sx, sy); } endShape(CLOSE); }